Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis - Quick Guide
Explore how artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis is transforming care. Learn key applications, benefits, and implementation tips.
Imagine a world where diseases are caught sooner and diagnoses are made with pinpoint accuracy. That world is no longer science fiction; it’s being built today, powered by artificial intelligence. This guide is all about how artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis is moving from a concept in a lab to a real, practical tool in clinics.
The New Frontier of AI in Medical Diagnosis
We're going to break down exactly how AI algorithms sift through complex medical data—think MRIs, CT scans, and extensive patient histories—with a speed and precision that was once unthinkable. It’s like having an expert consultant on your team who has already reviewed millions of cases, ready to offer insights that help a doctor make the final call.
The goal here isn't to replace a physician's expertise. It's to enhance it. This creates a powerful partnership between the clinician and the machine, promising to make the entire diagnostic process faster, more accurate, and ultimately, more accessible for everyone.

What Are The Core AI Technologies in Diagnosis?
So, what's actually happening under the hood? It all comes down to a few key technologies that have matured enough to handle the complexities of medical data. Each one plays a unique role, from finding hidden patterns to understanding clinical language.
The table below breaks down the main AI players and what they do in a diagnostic setting.
Key AI Technologies Driving Medical Diagnosis
| AI Technology | Primary Function in Diagnosis | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning (ML) | Pattern recognition and predictive analysis from structured data (e.g., lab results, vital signs). | Predicting sepsis risk in ICU patients based on real-time monitoring data. |
| Deep Learning (DL) | Advanced pattern detection in complex, unstructured data, especially medical images. | Identifying cancerous nodules in lung CT scans or diabetic retinopathy from retinal images. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Extracting and understanding meaningful information from clinical text (e.g., doctor's notes, patient records). | Analyzing electronic health records (EHRs) to identify patients eligible for a clinical trial. |
| Computer Vision | Interpreting and analyzing visual information from medical scans, slides, and videos. | Assisting pathologists by highlighting abnormal cells on a digital pathology slide. |
These technologies are the building blocks. When combined, they give clinicians a much clearer picture, helping them connect dots that were previously invisible.
Driving Forces Behind AI Adoption
The real momentum behind AI in diagnostics comes from its ability to process massive datasets that are simply too large for a human to manage effectively. To get a handle on how this works, it helps to understand the fundamental principles of machine learning. These algorithms are trained to spot incredibly subtle patterns—from microscopic changes in cells to faint anomalies on a scan—that the human eye might miss.
This is a game-changer in fields like oncology and neurology, where catching a problem early can make all the difference. The technology provides a consistent, data-driven layer of analysis that perfectly complements a physician's hands-on experience and intuition, as we explored in our AI adoption guide. You can see more on how these AI capabilities are making a broad impact across the healthcare industry.
The synergy between human intuition and machine precision is at the heart of this new diagnostic frontier. AI tools act as powerful amplifiers, enhancing a clinician's ability to make informed decisions quickly and confidently.
A Rapidly Growing Market
The industry’s confidence is clear when you look at the numbers. The global market for AI in diagnostics was valued at USD 1.94 billion in 2025 and is on track to hit USD 10.28 billion by 2034.
That's a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.37%. It’s a strong signal that healthcare systems are increasingly relying on AI-powered tools to get better results for patients. For any healthcare leader, this signals that the time for strategic planning is now. Building a smart approach to AI isn't just a futuristic idea anymore; it's a necessity for staying competitive and delivering the best care possible.
How AI Is Driving a Leap Forward in Diagnostic Accuracy
When we talk about artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis, we're not talking about replacing doctors. We're talking about giving them a powerful partner—a tool that can sift through enormous amounts of information at incredible speeds, spotting subtle patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed. This collaboration is where the magic happens, pushing diagnostic accuracy to new levels.
Think about a radiologist looking at a CT scan or a pathologist examining a tissue slide. These are highly trained experts, but the sheer volume of data can be overwhelming. An AI platform can analyze that same scan or slide in minutes, not hours. This incredible speed helps teams triage critical cases, shorten the agonizing wait for patients, and make the entire diagnostic process far more efficient.
Seeing the Unseen in Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is where AI is already making a huge difference. Imagine the challenge of finding a tiny, cancerous nodule in a lung scan or catching the very first signs of diabetic retinopathy in a retinal photo. It’s like finding a needle in a haystack.
AI algorithms, however, can be trained on millions of these images. They learn the distinct visual signatures of a disease and can spot them with an almost uncanny consistency. The technology acts as a tireless, unbiased second set of eyes, reducing the risk of human error that can come from fatigue or a crushing caseload. By handling the repetitive, analytical heavy lifting, AI frees up specialists to focus on what they do best: complex patient care and treatment planning.
The Proof Is in the Performance
The evidence is mounting, and it’s pretty compelling. Across various medical fields, AI is consistently performing at a level that matches—and sometimes even surpasses—human experts.
Take a significant South Korean study on breast cancer detection. An AI system achieved an impressive 90% sensitivity in finding breast cancers with masses. In the same test, radiologists reached 78% sensitivity. The AI also proved better at early detection, hitting 91% accuracy compared to the radiologists' 74%. These numbers aren't just statistics; they represent lives that can be saved.
By consistently checking medical data against millions of learned examples, AI brings a new level of precision to diagnostics. This helps standardize care and reduce the differences in diagnoses from one clinician to another.
This kind of performance shows how AI can serve as a vital safety net in the diagnostic workflow.
From Raw Data to a Clear Diagnosis
So, how does it actually work? The process starts by training an AI model on a huge, carefully prepared dataset of medical images. For instance, thousands of chest X-rays are labeled as either "normal" or "pneumonia." The algorithm meticulously learns the visual traits tied to each condition. Once it's trained, the model can look at a brand-new image and give a probability score for whether a disease is present.
This capability is being built into practical tools that are improving how clinicians work every day. Here are just a few real-world examples:
Radiology: AI can automatically outline organs, measure tumors, and flag suspicious spots on CT and MRI scans for a radiologist to review.
Pathology: Specialized algorithms analyze digital slides to count cells, spot mitotic figures, and grade tumors, giving pathologists hard data to back up their assessments.
Dermatology: AI models analyze pictures of skin lesions to help tell the difference between benign moles and dangerous melanomas, which is crucial for early detection.
These aren't futuristic concepts; they are becoming essential parts of modern medicine. For any organization wanting to explore these kinds of applications, a tool like Ekipa AI's Diagnoo AI Business Idea Validation tool can be invaluable for figuring out the feasibility and potential impact of a specific diagnostic idea. Using these powerful AI solutions allows healthcare providers to make better, faster decisions.
Where AI is Making a Real Difference in Medical Specialties
The real story of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis isn't in the theory; it's in the clinic, at the patient's bedside. When you look at how AI is being used across different medical fields, you see it's not some far-off concept—it's a practical tool delivering real results today. These are highly specific algorithms built to solve distinct clinical problems, making a genuine impact on patient outcomes and a physician's daily work.
We're talking about everything from reading complex scans to forecasting how a disease might progress. The most successful real-world use cases aren't generic, one-size-fits-all platforms. They are specialized systems, meticulously trained to be exceptionally good at a single diagnostic job. This focused approach is precisely why they're so effective at supporting, not replacing, human expertise.
Radiology and Medical Imaging
If there's one area where AI's impact is impossible to miss, it's radiology. Think of AI as a tireless, incredibly precise assistant for radiologists. These algorithms can sift through X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with a speed and consistency that humans simply can't match.
Anomaly Detection: AI models are excellent at flagging suspicious areas, like potential tumors or tiny fractures, that need a second look. This helps radiologists prioritize the most critical cases and acts as a vital safety net.
Image Segmentation: Manually outlining organs or lesions on a scan is a tedious, time-consuming task. AI can do it automatically in seconds, providing the exact measurements needed for planning treatments and tracking progress.
This isn't about replacing the radiologist. It’s about clearing their plate of repetitive tasks so they can dedicate their expertise to the most complex cases and patient consultations. It’s a perfect example of how the right AI tools for business can dramatically improve an expert’s workflow.
Oncology Precision and Prediction
In cancer care, every minute and every piece of information matters. AI is making a huge contribution here by digging through massive datasets to give oncologists a much deeper understanding of a patient's specific cancer.
For instance, AI can analyze digital pathology slides to identify and classify cancer cells, often spotting subtle patterns that are invisible to the naked eye. This helps pathologists grade tumors more accurately and consistently. Even better, by looking at a patient's genomic data and clinical history, AI can help predict which treatments are most likely to work, pushing medicine closer to truly personalized care.
By processing immense datasets, AI helps oncologists move beyond a one-size-fits-all approach. It supports the shift toward tailored treatment plans based on a tumor's unique characteristics and the patient's individual profile.
Cardiology and Proactive Heart Health
The power of AI in cardiology lies in its ability to see the future in today's data. By analyzing electrocardiograms (ECGs) and other cardiac signals, these models can pick up on faint irregularities that are tell-tale signs of a high risk for a future heart attack or arrhythmia.
This predictive insight is a game-changer. It allows doctors to step in before a crisis happens, recommending lifestyle changes or starting preventative treatment. Getting these tools to work seamlessly within a hospital's existing IT environment often depends on solid custom healthcare software development.
Neurology and Early Disease Detection
Neurological conditions like Alzheimer's disease or stroke often begin with tiny changes that are incredibly hard to spot early on. AI is changing that. By analyzing brain scans like MRIs and PET scans, algorithms can identify the earliest signs of neurodegeneration.
The system works by comparing a patient's scan to a database of thousands of others, allowing it to detect subtle shifts in brain volume or activity long before a person shows obvious symptoms. Finding the disease early is absolutely critical for managing its progression and giving patients a better quality of life. The underlying tech to support this is complex, and understanding the broader ecosystem of IT services tailored for the healthcare sector is key. Moving from a clinical need to a deployed solution shows just how important a clear roadmap, often developed through expert AI strategy consulting, truly is.
8. Common Pitfalls and How to Sidestep Them
The promise of using artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis is enormous, but getting from a great idea to a tool clinicians actually use is a journey fraught with challenges. It’s not just about the tech. Success hinges on a clear-eyed understanding of the real-world hurdles, from messy data to complex hospital politics.
One of the first brick walls teams hit is data. AI models are hungry, and they need a diet of high-quality, diverse, and well-labeled data to learn effectively. In healthcare, finding that data is a huge challenge, especially while navigating the tight privacy and security rules of regulations like HIPAA.
The "Black Box" Problem: Why Trust Is Everything
A huge obstacle to getting doctors on board is the "black box" problem. Many powerful AI models are great at finding patterns and making predictions, but they can't explain how they reached a conclusion. A doctor isn't going to bet a patient's health on a recommendation from a machine if they can't understand its reasoning. It's as simple as that.
This is why there's such a big push for Explainable AI (XAI). Clinicians need to see the "why" behind the "what." Knowing why an AI flagged a tiny spot on a lung scan as potentially cancerous is what builds the trust needed for real-world adoption. Without that transparency, even the most brilliant algorithm will just sit on a server, unused.
Getting Through Regulatory Mazes and IT Headaches
Launching a diagnostic AI tool isn't like releasing a new app. These tools are often treated as medical devices, meaning they have to get through tough regulatory bodies like the FDA. This is a long, expensive process that requires rock-solid proof that the tool is both safe and effective.
Then there's the technical side. Hospitals run on a complex web of existing systems, with the Electronic Health Record (EHR) at the center. Any new AI tool has to plug into these workflows without causing chaos.
A tool that forces a radiologist to log into a separate system or manually re-enter patient data is dead on arrival. It creates friction, slows them down, and will be abandoned almost immediately. True value comes from seamless integration.
This is why a structured plan is absolutely critical. You have to start by mapping out the entire ecosystem and defining exactly what you need the AI to do.
A Practical Guide to Avoiding Common Stumbles
Thinking ahead is the best way to navigate this complexity. Most organizations run into the same handful of problems, but with the right strategy, these can be managed or avoided entirely.
Below is a quick summary of the most common mistakes we see and how to get ahead of them.
Common Pitfalls in AI Diagnostic Implementation and How to Avoid Them
| Common Pitfall | Potential Impact | Strategic Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Data Quality | Inaccurate models, biased results that harm patient groups, and failure to pass validation. | Create a strong data governance plan from day one. Invest time and resources in cleaning, organizing, and annotating data correctly. |
| Ignoring Workflow Integration | Clinicians won't use it, patient care gets disrupted, and the entire investment is wasted. | Bring clinicians into the design process from the very beginning. Shadow them, ask questions, and build the tool to fit their world. |
| The 'Black Box' Issue | Deep distrust from medical staff, inability to troubleshoot errors, and major hurdles with regulatory approval. | Make explainability a priority. Choose models that can provide clear, understandable reasons for their outputs. |
| Forgetting About People | Staff resists the new technology, fears their jobs are at risk, and the tool never gets used to its full potential. | A solid change management plan is key. Communicate early and often, provide excellent training, and show how the tool helps, not replaces. |
Think of implementing AI in diagnostics as a marathon, not a sprint. It takes careful planning, getting everyone on board, and truly understanding the clinical environment you’re trying to improve.
A proven roadmap, like our AI Product Development Workflow, gives you the framework needed to move confidently from a promising idea to a successful clinical tool. By anticipating these challenges, healthcare leaders can build a foundation for an AI strategy that actually works.
Your Strategic Roadmap for AI Adoption
So, you understand the potential of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis. That's the easy part. The real work begins when you move from theory to practice, and that requires a thoughtful, deliberate plan. You can't just "turn on" AI; it's a journey that weaves together new technology with your existing people and processes. Without a clear roadmap, even the most exciting AI projects can stall out, never delivering on their promise.
The first, most crucial step is to get crystal clear on your goals. What, specifically, are you trying to fix or improve? Maybe you want to slash the turnaround time for radiology reports. Perhaps the goal is to boost the accuracy of early cancer detection or get better at predicting which patients are at high risk for a specific condition. Nailing down these precise, measurable objectives is the bedrock of your entire strategy.
Think of it as a three-stage process: first, you analyze your needs and resources. Then, you integrate the technology. Finally, you govern its use to ensure it remains safe, effective, and aligned with your goals.
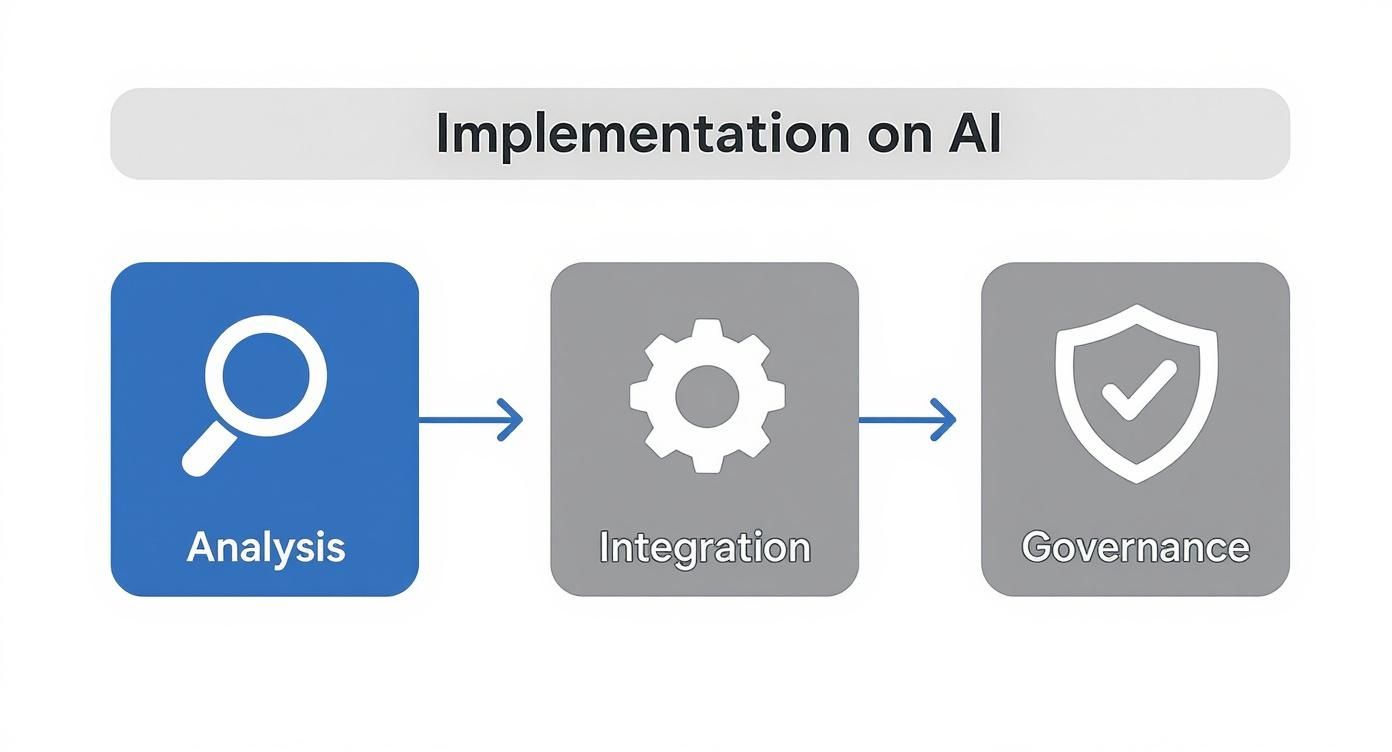
This isn't a one-and-done project. It's a continuous cycle of planning, doing, and overseeing to make sure the technology keeps serving your clinical needs.
Building the Foundation: Data and Infrastructure
With clear goals in hand, it's time to talk about data. An AI model is only as smart as the data it learns from, so taking a hard look at your data readiness is non-negotiable. This means digging into the quality, accessibility, and sheer volume of your clinical data. You also have to be honest about whether your current IT infrastructure has the muscle to handle the heavy computational lifting that AI demands.
Next up is a big decision: do you partner with an established AI vendor, or do you build your own internal tooling? Going with a vendor gets you up and running faster, but an in-house solution gives you total control and customization. There's no single right answer—it all comes down to your organization's budget, in-house expertise, and long-term vision. A detailed Custom AI Strategy report can be a huge help here, breaking down the pros and cons for your unique situation.
From Pilot Project to Full-Scale Deployment
Before you even think about a system-wide rollout, you need to run a pilot project. This is your chance to test the AI tool in a controlled, real-world clinical setting. A pilot proves the tool's value, validates its ROI, and—just as importantly—helps you spot workflow hiccups before they become massive headaches for everyone.
A pilot project is your proving ground. It’s where you move from theory to practice, demonstrating tangible value to stakeholders and building the momentum needed for broader adoption.
Getting from a successful pilot to a full-scale deployment hinges on one thing: change management. This is where so many initiatives stumble. You have to bring your clinical staff along for the ride. That means providing great training, listening to their concerns, and showing them how this tool will be a co-pilot, not a replacement. Building that trust is everything.
The Surge in Clinical Adoption
The good news is that these efforts are working. We're seeing a massive shift in how clinicians view these tools. Physician adoption of health AI has skyrocketed, with about 66% of doctors using AI in some form by 2024. That’s a staggering 78% jump from just 38% in 2023.
It’s not just doctors, either. An estimated 80% of hospitals are now implementing AI solutions to improve both patient outcomes and their own operational efficiency. These numbers tell a clear story: AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it's becoming a standard of care.
This rapid uptake highlights why having a solid plan is so critical. For healthcare organizations that want to get this right, partnering with an expert team for services like AI Automation as a Service can cut through the technical and operational complexity. As we've seen time and again, a thoughtful, phased approach is the key to truly transforming your diagnostic capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
It's natural to have questions when we talk about bringing artificial intelligence into something as important as medical diagnosis. Whether you're a doctor, a hospital administrator, or just curious, this is new territory for many. Let's tackle some of the most common questions head-on.
Will AI Replace Doctors and Radiologists?
That's probably the biggest question on everyone's mind, and the short answer is no. The consensus among experts is that AI is here to augment human expertise, not replace it.
Think of it this way: AI is like an incredibly sharp, fast, and tireless assistant. It can sift through mountains of data—like thousands of medical images—and flag potential issues with remarkable precision. This frees up doctors and radiologists to focus on what they do best: handling complex diagnoses, communicating with patients, and crafting the right treatment plan. AI provides a powerful second set of eyes, helping to catch things that might be missed and ultimately letting clinicians deliver even better care.
What Are the Biggest Challenges to Implementing AI in a Hospital?
Getting AI up and running in a clinical setting isn't as simple as installing new software. The real hurdles are a mix of technology, process, and people.
Some of the main challenges we see time and again are:
Data Quality: AI models are only as good as the data they're trained on. Sourcing high-quality, diverse, and unbiased data is a major undertaking.
System Integration: A new AI solution has to play nice with all the existing hospital systems, especially the Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This can be a significant technical puzzle.
Regulatory Hoops: Medical devices, including AI software, have to clear high bars set by bodies like the FDA. It's a complex and rigorous process.
Privacy and Security: Protecting patient data and ensuring HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable and adds layers of complexity.
Building Trust: Perhaps the most important piece is getting clinical staff on board. Doctors need to trust the technology and understand how it fits into their workflow.
A solid plan, like a Custom AI Strategy report, is essential for thinking through these technical, regulatory, and human factors from day one.
How Can a Healthcare Organization Get Started with AI for Diagnosis?
The key is to think big but start small. Trying to overhaul everything at once is a recipe for frustration.
A much smarter approach is to pick one specific, high-impact problem to solve first. An AI requirements analysis can help pinpoint a diagnostic area where AI could make a real, measurable difference. From there, you can launch a pilot project to test the technology, work out the kinks, and prove its value. Working with a partner that specializes in AI strategy consulting can provide a clear roadmap and help you make the right choices from the start.
Is AI in Medical Diagnosis Safe and Reliable?
When it’s done right, absolutely. AI tools intended for medical diagnosis go through incredibly strict testing and validation before they ever get near a patient. For many specific tasks, their reliability can match—or even beat—human performance.
But safety isn't a one-and-done deal. It requires constant vigilance. The best systems always keep a "human in the loop," meaning a qualified clinician has the final say. Ongoing monitoring and quality checks are crucial to make sure the AI performs as expected out in the real world. You can see how this works by looking at real-world use cases. To figure out how this could work for your organization, our expert team is always ready to help.