Deep Learning for Medical Imaging Analysis A Practical Guide
Explore how deep learning for medical imaging analysis is revolutionizing healthcare. This guide covers key models, real-world applications, and ROI strategies.
At its core, deep learning for medical imaging analysis is about teaching advanced AI models to read and interpret medical scans—think X-rays, CTs, and MRIs. These sophisticated algorithms learn to spot patterns, anomalies, and signs of disease, often with a precision that can match or even surpass the human eye. Think of it as a highly trained second pair of eyes for clinicians, helping them make faster, more confident diagnostic decisions.
The New Era of AI-Powered Medical Diagnostics
Picture a radiologist trying to find a tiny, early-stage tumor on a CT scan. It’s like searching for a specific face in a massive crowd. Deep learning acts like a spotlight, instantly highlighting areas that need a closer look. This is the fundamental shift happening in diagnostics today thanks to deep learning for medical imaging analysis.
These AI models are no longer just research projects; they are becoming practical tools integrated into daily clinical workflows. They aren't here to replace medical professionals but to augment their skills, helping them manage the sheer volume and complexity of modern imaging data. The benefits are real and are being felt across the entire healthcare system.
Driving Clinical and Commercial Growth
Deep learning is now the go-to technology in this field, and its impact is showing up in both patient care and market numbers. The global AI-in-medical-imaging market was valued at around USD 1.36 billion in 2024. It’s expected to surge to USD 19.78 billion by 2033, which is a massive compound annual growth rate of about 34.7%. North America is currently leading the charge, holding over 45% of the market share, thanks to focused R&D and a clearer path to regulatory approval.
This incredible growth shows just how much value hospitals, clinics, and med-tech companies see in this technology. The advantages are straightforward and compelling:
- Faster, More Accurate Diagnoses: An AI can sift through thousands of images in the time it takes a human to review a few, flagging subtle details that might otherwise be missed.
- More Efficient Workflows: By taking over routine tasks like measuring lesions or annotating scans, AI gives clinicians more time to spend on challenging cases and with their patients.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: When you can detect diseases earlier and more accurately, you can start the right treatment sooner, which almost always leads to better results.
To get a fuller picture of this shift, it helps to explore the wider trends in how AI for medical imaging and diagnostics is reshaping the industry. In this guide, we’ll break down the essential techniques, show you where they’re making the biggest impact, and lay out a practical roadmap for implementation, showing how our Healthcare AI Services can help you get there faster.
Understanding the Core Deep Learning Models
To get a real handle on deep learning in medical imaging, we need to look under the hood at the engines driving this technology. These models are the "brains" of the operation, each with unique strengths tailored for different clinical challenges. It helps to think of them not as abstract algorithms, but as highly specialized tools, each designed for a specific medical job.
This section will pull back the curtain on the core models—from the foundational to the more advanced—without getting lost in the technical weeds. By understanding what they do and how they "think," you'll see how custom AI solutions can be built to solve tangible diagnostic problems in a clinical setting.
Convolutional Neural Networks: The Visual Cortex of AI
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the undisputed workhorses of medical image analysis. You can think of a CNN as the AI’s visual cortex, engineered specifically to "see" and recognize patterns in images, much like our own brains do when we process visual information.
A CNN learns in layers. It starts by identifying simple features in a medical scan—things like edges, corners, and basic textures. It then builds on this, combining these simple elements into more complex structures, like the distinct outline of an organ or the specific texture that signals a lesion. This hierarchical process lets it assemble a complete picture, piece by piece, until it can confidently classify an image as, say, containing a malignant or benign tumor.
This ability to automatically learn important features directly from raw pixel data is what makes CNNs so powerful. Older machine learning methods needed human experts to painstakingly define what the algorithm should look for. CNNs figure it out on their own. Our Healthcare AI Services often build on a CNN foundation to create exceptionally robust diagnostic tools.
Transformers and VLMs: The Clinical Context Engine
While CNNs are brilliant at spotting what is in an image, the next generation of models is all about a deeper level of understanding. Transformers and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) act less like a visual cortex and more like an experienced clinician who instinctively connects visual evidence with other patient data.
Transformers, which first made waves in natural language processing, are exceptionally good at understanding context and seeing the big picture. When applied to medical imaging, this means they can analyze an entire scan holistically, grasping how different regions of an image relate to one another.
Vision-Language Models take this a giant leap further. They connect the visual data from an image with the textual data from a patient's electronic health record (EHR). A VLM doesn't just see a fracture on an X-ray; it can read the radiologist's notes, process the patient's reported symptoms, and synthesize all of it to offer a far more comprehensive analysis.
This multimodal capability is a massive step forward. It moves AI beyond simple pattern recognition and toward becoming a more nuanced, context-aware partner in diagnostics. Building these sophisticated models is a core part of our AI Product Development Workflow, ensuring our solutions are not just accurate, but genuinely clinically relevant.
Comparing Key Deep Learning Models
To select the right tool for a specific clinical job, you have to know the key differences between these architectures. A smart AI strategy consulting approach always starts by matching the problem to the right technology. Here’s a quick comparison to help clarify their core functions and best-fit applications.
Comparison of Key Deep Learning Architectures for Medical Imaging
This table contrasts the most common deep learning models used in medical imaging, outlining their primary functions, best-suited applications, and typical data needs to help stakeholders understand the technology landscape.
| Model Architecture | Core Function | Primary Medical Imaging Use Cases | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNNs | Hierarchical pattern recognition from pixel data. | Lesion detection, organ segmentation, image classification (e.g., benign vs. malignant). | High accuracy in visual tasks with large, labeled datasets. |
| Transformers | Contextual analysis of relationships across an entire image. | Analyzing whole-slide pathology images, identifying diffuse diseases like pneumonia. | Superior at capturing global context compared to the local focus of CNNs. |
| VLMs | Fusing visual data with text from clinical notes. | Generating automated radiology reports, answering clinical questions about scans. | Provides rich, multimodal understanding that mirrors a clinician's reasoning. |
As you can see, each model plays a unique and valuable role. From the sharp visual acuity of CNNs to the sophisticated contextual reasoning of VLMs, these technologies form a powerful toolkit. The real key to success isn't just having these tools, but knowing precisely how and when to apply them to improve patient outcomes and streamline clinical workflows. Getting this right always begins with a detailed AI requirements analysis to ensure the technology is perfectly aligned with clear clinical goals.
Where AI Makes a Real-World Difference in Patient Care
Technology is only as good as its real-world impact. In healthcare, that means improving patient outcomes, making life easier for clinicians, and finding efficiencies in packed hospital schedules. Deep learning for medical imaging analysis is already making that leap from the lab to the clinic, delivering real value in a growing number of specialties.
This isn't science fiction. Think about a busy emergency room. An AI tool flags a potential stroke on a brain scan the second it's complete, pushing it to the top of the radiologist’s worklist. That simple act of prioritization can shave off precious minutes—even hours—and completely change a patient’s prognosis. These are the kinds of powerful, practical applications that show what AI can do in medicine right now.
High-Impact Applications Across Medical Fields
Deep learning isn't a one-trick pony. Its real strength is its adaptability, with algorithms being fine-tuned to solve specific problems across many different fields of medicine.
- Oncology: In cancer care, AI models can automatically find and outline tumors on CT or MRI scans. This gives oncologists a perfectly consistent way to track tumor growth or shrinkage, offering clear, objective proof of whether a treatment is effective. Our own tool, Diagnoo, is built to provide this kind of advanced diagnostic support.
- Cardiology: When it comes to heart health, deep learning can analyze cardiac MRIs to calculate ventricle volume and ejection fraction—critical metrics for assessing heart function. This automated process is faster and, just as importantly, removes the natural variability you see when different clinicians take the same measurements.
- Orthopedics: AI algorithms are now able to spot subtle, hairline fractures on X-rays that the human eye might miss, especially in anatomically complex areas like the wrist or ankle. This means a faster diagnosis, quicker treatment, and less risk of long-term complications.
What these examples show is that AI is best used as a powerful partner for clinicians, not a replacement. It takes on the heavy lifting of data analysis and repetitive tasks, which frees up doctors to focus on what they do best: making complex judgments and caring for their patients.
It’s Not Just About Diagnosis—It’s About a Smarter Workflow
While a more accurate diagnosis is a huge win, the benefits of deep learning ripple out across the entire clinical workflow. Smart systems are helping to streamline how medical imaging departments run, creating efficiencies that help the whole hospital. These efficiencies are often part of a broader AI Automation as a Service strategy.
One of the biggest wins is intelligent triage. AI models can pre-screen an entire queue of imaging studies, automatically flagging urgent cases for immediate review. This ensures that a patient with a pulmonary embolism gets attention before someone with a routine follow-up, which directly improves outcomes in time-sensitive situations.
Another key area is quantitative analysis. Manually measuring the change in a lesion’s size or tracking tissue density over time is tedious and can vary from one person to the next. AI provides precise, repeatable measurements, giving clinicians solid, objective data to monitor diseases and treatment responses. That consistency is gold, both for everyday patient care and for formal clinical trials.
By automating these critical but time-consuming tasks, deep learning doesn't just make diagnostics more accurate; it makes the entire system more efficient. This allows healthcare providers to handle growing caseloads without sacrificing quality of care.
At the end of the day, these applications prove that deep learning is much more than just a clever algorithm. When applied with a clear purpose, it becomes a core part of modern medicine, enhancing the skills of clinicians and leading to better outcomes for patients. The secret is matching the right technology to the right clinical problem—a principle that drives everything we do.
Navigating Critical Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
Adopting deep learning for medical imaging isn't just a technical challenge; it comes with a tremendous amount of responsibility. While the algorithms are powerful, getting them safely into a clinical setting means wading through a complex world of regulations, privacy laws, and ethical minefields. These non-technical hurdles are every bit as important as the model's accuracy, and they're a cornerstone of any effective AI strategy consulting engagement.
To bring an AI-powered diagnostic tool to market, you have to meet the demanding standards of regulatory bodies. In the United States, that means getting clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In Europe, devices need a CE marking to prove they meet strict safety and performance rules. This isn't a simple rubber stamp—the approval process is tough, requiring a mountain of documentation, thorough clinical validation, and solid proof that the tool is both safe and effective.
The good news is that the pace is picking up. Since 2020, we've seen a sharp increase in regulatory approvals and clinical use of AI in medical imaging. By mid‑2025, the U.S. FDA had cleared around 873 radiology AI tools. In the first part of 2025 alone, about 115 new radiology algorithms were added—that's a jump of more than 15% from the end of 2024. This explosion is heavily concentrated in radiology, which made up roughly 78% of new AI medical device approvals early in the year. You can dive deeper into these AI radiology trends to see where the field is heading.
Protecting Patient Data Is Non-Negotiable
Beyond getting regulatory sign-off, data governance is the absolute foundation of any medical AI project. Patient data is profoundly sensitive, and protecting it isn't optional; it's a legal and ethical duty. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. sets the gold standard for safeguarding this information.
But compliance is more than just having secure servers. It's about having airtight protocols for handling data at every single step, from the moment it's collected to when it's used for training and deployment. Key practices include:
- Secure De-identification: This means systematically stripping all personally identifiable information (PII) from medical images and records before they ever touch a training algorithm.
- Anonymization: Taking it a step further, anonymization makes it impossible to trace data back to an individual, offering the strongest possible privacy shield.
- Access Control: You need strict rules that ensure only authorized people can access sensitive data, and only for clearly defined, approved reasons.
Getting data governance right is essential for earning trust from patients and staying on the right side of the law. This is where expertise in custom healthcare software development becomes invaluable, ensuring these protections are baked in from day one.
Addressing Algorithmic Bias and Ensuring Oversight
Finally, we have to talk about the ethical tightrope. An AI model is only as good—and as fair—as the data it learns from. If your training dataset is skewed toward one demographic, the algorithm will likely underperform for everyone else. This isn't just a technical flaw; it risks making existing health disparities even worse.
This is why tackling algorithmic bias is a critical ethical responsibility. It means actively curating diverse, representative datasets and constantly testing the model’s performance across different populations to ensure it's fair for everyone.
And even with the most accurate AI, the final call should never be left to a machine. The principle of human-in-the-loop oversight is absolutely crucial. Think of the AI as a highly skilled assistant that can flag potential issues and provide hard data, but the ultimate diagnosis and treatment plan must remain in the hands of a qualified clinician. They provide the context, empathy, and holistic judgment that an algorithm simply can't. Making sure this partnership works seamlessly is a key part of our AI Product Development Workflow.
How Do You Measure Success and Calculate the Real ROI?
For any healthcare leader, bringing deep learning into medical imaging has to do more than just work on a technical level—it needs to deliver real, tangible value. While metrics like model accuracy are a good start, the true measure of success is found in the business and clinical outcomes that make the organization stronger. It's about moving beyond the algorithm to see the actual return on investment (ROI).
Figuring out that ROI starts with connecting the technology to the key performance indicators (KPIs) that really matter to your hospital or clinic. Instead of just asking, "Is the AI right?" we need to be asking, "How does this make our care better and our operations smoother?" A solid AI strategy consulting approach always begins by setting these critical benchmarks from day one.
Key Performance Indicators That Actually Mean Something
To build a business case that gets everyone on board—from clinicians to administrators to the finance team—you need to focus on metrics that resonate with all of them. These are the KPIs that show the practical, day-to-day benefits of adding advanced AI tools for business to your diagnostic workflows.
Here’s what you should be measuring:
- Clinical Efficiency: How long does it take to get a report back? Tracking the average report turnaround time (TAT) is crucial. A significant drop here means doctors get information faster, and patients get treatment decisions sooner.
- Operational Throughput: Look at how you're using your expensive equipment. Are your scanners sitting idle? If an AI tool helps radiologists clear their queue faster, you can see more patients each day without buying a single new machine.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: This one is huge for patient safety. Monitor things like diagnostic error rates or disagreements between the initial AI-assisted read and the final one. Any measurable improvement here is a direct win for care quality.
- Patient Outcomes: This can be trickier to tie directly to the AI, but it's not impossible. Look at metrics like the length of a hospital stay or readmission rates for conditions where a fast, accurate diagnosis is everything (like a stroke).
Calculating a Realistic Return on Investment
Working out the ROI for a deep learning solution is a balancing act. You have to weigh the upfront and ongoing costs against the financial gains you get from being more efficient and providing better care. And the good news is, clinical impact studies show these benefits are very real.
For example, in some workflows, AI-powered models helped scanners operate up to 80% faster without sacrificing image quality. On the financial side, a 2024 analysis found that 79% of healthcare organizations using AI saw an average return of $3.20 for every $1.00 they invested. Much of that return was driven by imaging use cases that streamlined workflows. You can dig deeper into the changing face of medical imaging to see how these trends are playing out.
So, how would you estimate this for your own organization? Let’s walk through a quick example for a mid-sized hospital’s radiology department:
1. Tally Up the Costs: * Upfront: This includes things like software licenses, the cost of integrating with your PACS/EHR systems, and getting your staff trained. * Ongoing: Don't forget annual subscription fees, IT maintenance, and the resources needed for continuous quality monitoring.
2. Map Out the Gains: * Efficiency Savings: How much is a radiologist's time worth? Calculate the value of the time saved each day, which can be redirected to more complex cases or simply allow for higher reading volumes. * New Revenue: Could you perform more scans or even offer new, advanced diagnostic services that weren't possible before? * Cost Avoidance: This is a big one. Think about the financial impact of catching a diagnostic error early. It can lower malpractice risk and prevent the need for much more expensive treatments down the road.
When you frame the investment this way, it stops being a conversation about a technology expense and becomes a strategic business decision. A Custom AI Strategy report can help your organization put hard numbers to these potential returns.
At the end of the day, a strong business case is built on clear, measurable outcomes. It's about showing how deep learning doesn't just make images better—it makes the entire system of care better. For more inspiration, check out some real-world use cases where AI is already making a difference. If you're ready to build your own case, our expert team is here to help guide you.
Your Roadmap for Implementing Medical Imaging AI
Jumping into a deep learning project for medical imaging isn't something you do on a whim. It demands a clear, structured plan. The most successful projects don’t start with technology—they start with a well-defined clinical problem and end with a fully integrated solution that delivers real, measurable value. This roadmap breaks down the process into logical phases, making sure your strategy solves a genuine clinical need while hitting your business goals.
The whole thing kicks off by identifying a specific, high-impact challenge in a clinical workflow. Is the ER struggling with slow turnaround times for stroke detection? Are oncologists dealing with inconsistent measurements of tumor response? Once you pinpoint the problem, a thorough analysis is needed to define what success looks like. This initial step sets the stage for everything that follows.
Phased Implementation for Sustainable Success
A methodical, step-by-step approach is the only way to go. It minimizes risk and dramatically increases the odds of clinicians actually adopting the tool. Rushing to deployment without rigorous validation is a classic recipe for failure, a topic we covered in our guide to enterprise AI adoption. A more deliberate process ensures the final product is safe, effective, and fits naturally into the daily grind.
Here’s a practical, phased plan to guide you:
- Data Preparation and Curation: This is the bedrock of your entire project. It involves gathering, de-identifying, and carefully annotating a high-quality dataset. Honestly, poor data quality is the single biggest reason AI projects in healthcare go belly-up.
- Model Selection and Pilot Testing: Next, you pick the right deep learning model for the specific task and train it on your curated data. But before you even think about a wide-scale rollout, you must run a small, controlled pilot test to see how it performs in a limited, real-world clinical setting.
- Integration and Workflow Optimization: The model has to plug smoothly into existing systems like PACS and EHRs. The goal is to augment the current workflow, not blow it up. We’ve managed this process for many clients; you can learn more about how it’s done at our guide on implementation support.
- Full-Scale Deployment and Monitoring: Once the pilot proves successful, you can roll the solution out more broadly. But the work isn’t over. Continuous performance monitoring is crucial to catch any "model drift" and ensure the tool remains accurate and safe long after launch.
This diagram shows the simple but powerful logic behind any AI initiative: invest wisely, implement correctly, and measure the return.
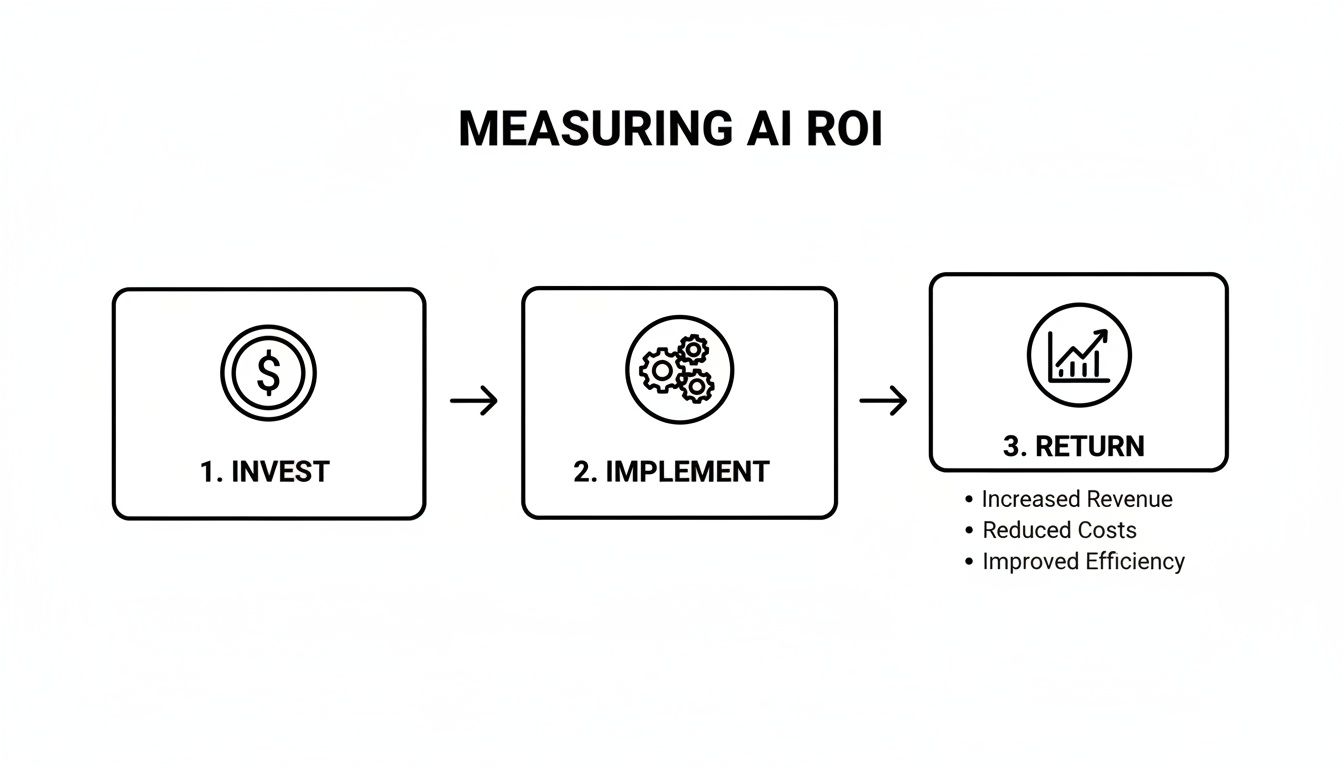
The key takeaway here is that the "return" isn't just about money. It's a powerful combination of efficiency gains, better diagnostic accuracy, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes.
The Power of Partnership
Pulling this off requires a tight-knit collaboration between clinicians, IT professionals, data scientists, and regulatory experts. It’s a lot to manage internally. Partnering with a team that has hands-on experience in deploying practical AI solutions for healthcare can seriously accelerate the entire process, helping you avoid common pitfalls.
By following this roadmap, you have a clear, step-by-step plan to get started. When you're ready to bring in the right expertise to guide you through it, our team is here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Diving into deep learning for medical imaging often brings up a lot of questions. We get it. Here are some straightforward answers to the things we hear most often, clearing up the role of this technology in modern medicine.
What Is the Difference Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Medical Imaging?
Think of machine learning (ML) as the broad category of algorithms that learn from data. In the old-school ML approach to imaging, a human expert would have to sit down and manually define the important features—things like tumor texture or lesion shape—before feeding them to the algorithm. It was a very hands-on process.
Deep learning (DL) is a more advanced subset of ML that cuts out that manual step. It uses sophisticated neural networks to figure out the important features all on its own, directly from the raw pixels of an image. This is why DL models are so good at spotting subtle, complex patterns that even a trained human eye might overlook.
How Much Data Is Needed to Train a Medical Imaging AI Model?
There’s no magic number here. The amount of data you need really depends on the task at hand. A relatively simple job, like classifying an image as cancerous or benign, might get by with a few thousand high-quality, annotated images. Something more complex, like precisely outlining a tumor in 3D, could easily require tens of thousands.
The good news is that techniques like transfer learning can dramatically reduce those numbers by letting us start with a model that’s already been trained on a massive image dataset. But remember, the quality of your data—meaning clean, consistent, expert-level annotations—is always just as important as the quantity.
Will AI Replace Radiologists?
The overwhelming consensus is no. The goal is to augment radiologists, not replace them. Deep learning is fantastic at handling specific, often repetitive, tasks like flagging potential nodules or measuring anatomical structures. This frees up specialists from the more tedious parts of their work.
This allows radiologists to spend their valuable time on the most complex cases, collaborating with other physicians, and focusing on direct patient care.
The future here is a partnership. AI becomes a powerful co-pilot, handling the grunt work so clinicians can focus on exercising their holistic judgment and delivering compassionate care—a core principle of our Healthcare AI Services.
What Are the Biggest Challenges to Deploying AI in a Clinical Setting?
The biggest hurdles almost always come down to three things: integration, validation, and regulation.
First, you have to get the AI to talk to the existing hospital IT systems, like PACS and EHRs. This is often a bigger technical lift than people expect, and it has to be done without disrupting established clinical workflows. Then, you absolutely have to validate the model's performance on your specific patient population and imaging equipment. A model trained in one hospital might not work as well in another without recalibration.
Finally, you have to navigate the regulatory maze with bodies like the FDA, which demands rigorous documentation and proof of safety and effectiveness. Getting through these challenges takes a dedicated, multidisciplinary team and a solid implementation strategy, which is exactly where our expert team comes in.
Ready to see what this could look like in your own diagnostic practice? At Ekipa AI, we build custom AI solutions that fit right into your clinical workflows, delivering real improvements in efficiency and accuracy. Explore our AI solutions and let's start the conversation.