A Guide to Building Your Healthcare Data Interoperability Strategy
Build a future-proof healthcare data interoperability strategy with our guide. We cover goals, FHIR standards, security, and a practical implementation plan.
A healthcare data interoperability strategy is your organization's game plan for making sure different health IT systems can actually talk to each other. It’s about ensuring that critical patient information can be accessed, exchanged, and used without a hitch. This isn't just a tech project; it's a fundamental shift to treating data as one of your most valuable assets for improving patient care, cutting costs, and creating a more resilient organization.
Why You Can't Afford to Ignore Interoperability
When healthcare data is stuck in different systems, it's not just a technical problem—it's a direct threat to patient safety and your bottom line. These data silos create blind spots in patient care and bog down your operations with massive inefficiencies.
Let’s walk through a scenario that plays out in hospitals and clinics every single day.
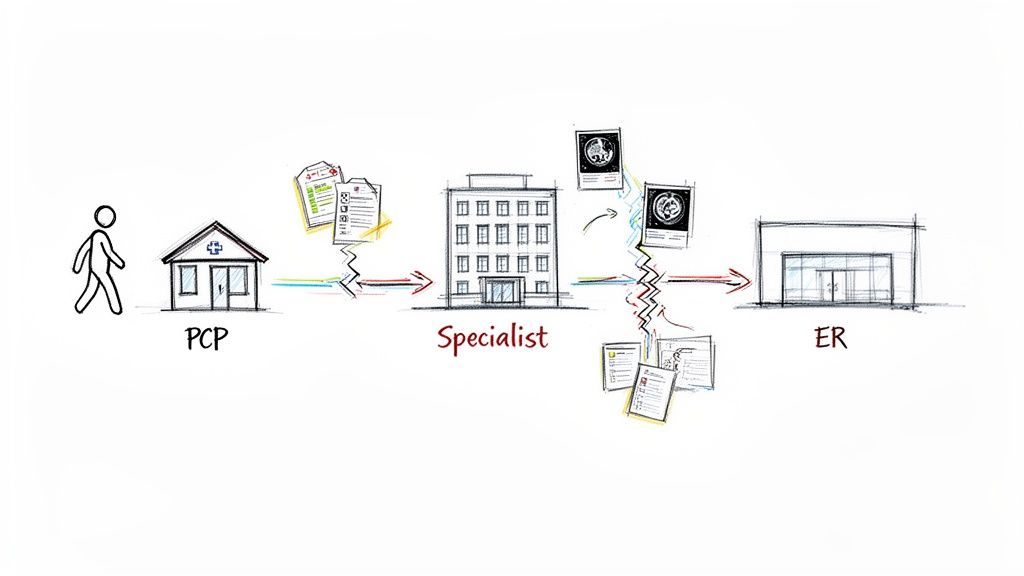
A patient sees their primary care physician (PCP) about a concerning health issue. After some initial tests, the PCP refers them to a specialist. The problem? That specialist uses a different Electronic Health Record (EHR) system and can't easily pull up the PCP's notes or lab results. Getting that information means dealing with faxes, endless phone calls, or relying on the patient to remember complex medical details.
Now, fast forward a few weeks. The patient has a sudden, serious episode and lands in an emergency room at a hospital that's part of yet another health system. The ER doctors are flying blind. They have no quick way to see the patient’s history, known allergies, or the recent findings from the PCP and the specialist.
The Real-World Consequences of Data Silos
This kind of fragmentation forces clinicians to make critical decisions based on an incomplete picture. The fallout is serious and far-reaching:
- Risks to Patient Safety: Lacking a complete medical history, the ER team might order a redundant CT scan—exposing the patient to unnecessary radiation and cost—or prescribe a drug that interacts dangerously with something they're already taking.
- Crippling Inefficiency: Staff at the PCP's office, the specialist's clinic, and the ER all waste precious time hunting down records. This isn't just frustrating; it delays care and inflates administrative costs. We're talking about hundreds of billions in administrative waste across the U.S. healthcare system every year.
- A Terrible Patient Experience: The patient has to tell their story over and over, fill out the same forms, and even repeat uncomfortable tests. It’s a frustrating process that erodes trust in the very system that’s supposed to be helping them.
A truly effective healthcare data interoperability strategy isn't about ticking a compliance box. It's about building a connected ecosystem where patient data flows securely and intelligently, giving clinicians the information they need to provide the best care at every turn.
This guide is designed to give you an actionable framework to move from fighting daily data fires to proactively building a strategy that turns information into a core asset. The ultimate goal is to connect this complex technical challenge to real-world wins: better patient outcomes and a healthier bottom line for your organization. By breaking down data silos, you can directly improve both clinical and financial performance. As you start this process, exploring what's possible with modern Healthcare AI Services can unlock even more powerful ways to use your newly connected data.
Building the Business Case and Aligning Stakeholders
Before a single line of code is written or a server is configured, a successful interoperability strategy starts with a conversation. It's about building a rock-solid business case that gets the C-suite excited and pulls every department—from the clinic floor to the billing office—onto the same page. Without that shared vision and buy-in, even the most technically elegant plan will stall out, starved of resources and support.
The trick is to stop talking about IT and start talking about outcomes. Your CFO doesn't really care about FHIR APIs. What they do care about is chipping away at the $265 billion lost every year to administrative bloat. A doctor on the front lines isn't thinking about data standards; they're thinking about the risk of making a decision with only half of a patient's story.
Quantifying the Return on Investment
To get executives to sign the checks, you need to speak their language: money and efficiency. This means creating a clear, compelling model that draws a straight line from your interoperability project to tangible financial and operational gains.
Your business case needs to be built on hard numbers.
- Slash Redundant Costs: How much are you spending on duplicate lab tests or imaging scans simply because clinicians can't see what was done at another facility? A unified patient view means a radiologist instantly sees a CT scan from down the street, preventing an expensive and unnecessary repeat procedure.
- Boost Staff Productivity: Clock the hours your clinical and admin teams burn every week chasing down records with phone calls and fax machines. Automating that data exchange frees up highly skilled people to focus on patient care, not paperwork.
- Accelerate Revenue: Show how a smooth flow of data can unclog the revenue cycle. When a patient’s insurance and treatment codes are correct and instantly available, claim denials plummet and cash flow improves.
This isn’t just a nice-to-have anymore; it's a global imperative. A staggering 84% of healthcare organizations now view interoperability as a core component of patient care. That conviction is fueling major investments, with the market expected to hit USD 4.5 billion by 2026. The driver is simple: the math works.
Translating Value for Every Stakeholder
A truly powerful business case is a chameleon—it changes its colors to match the person you're talking to. You're not just building a system; you're building a coalition. And that means you have to frame the benefits in a way that resonates with each department’s biggest headaches and highest priorities.
A one-size-fits-all pitch is doomed to fail. What gets the Chief Medical Officer on board is entirely different from what motivates the head of compliance.
Here’s a practical way to think about tailoring your message:
| Stakeholder Group | What Keeps Them Up at Night? | How Interoperability Solves It (Your Pitch) |
|---|---|---|
| Clinicians (Doctors, Nurses) | Patient Safety & Wasted Time | "Get a complete patient history in seconds. Make safer, faster decisions and reclaim the time you're losing to administrative busywork." |
| Finance (CFO, Billing) | Costs & Leaky Revenue | "Let's plug the holes. We can eliminate millions in redundant tests and speed up payments by cutting claim denials." |
| IT Department (CIO, CTO) | Security & Tech Debt | "We can build a modern, secure data backbone that eliminates brittle, point-to-point fixes and is built to scale for the future." |
| Legal & Compliance | Risk & Regulatory Penalties | "This ensures fully auditable, compliant data sharing that nails HIPAA and 21st Century Cures Act rules, protecting the entire organization." |
By translating the technical goals into specific solutions for real-world problems, you get everyone pulling in the same direction. This stakeholder-centric approach is the same principle behind a strong Custom AI Strategy report, ensuring any plan is grounded in what the organization actually needs to succeed. Building this coalition isn’t just step one; it’s the most important step in making your strategy a reality.
Choosing Your Technical Foundation and Architecture
To build a durable interoperability strategy, you first have to get the technical groundwork right. This is about more than just picking the latest technology; it’s about defining the architectural DNA that will dictate how flexibly and securely your organization can share data for years to come. Making the right choices here prevents costly rework down the road and sets you up to handle whatever comes next.
At the technical core of interoperability is a shared language, or a set of data standards. Think of them as the grammar that lets different systems understand each other. Without them, you just have digital noise.
Demystifying Core Data Standards
For decades, healthcare has relied on a handful of key standards, each built for a specific job. If you want to design a system that bridges the old with the new, you have to know what they are and where they fit.
- HL7v2 (Health Level Seven version 2): This is the undisputed workhorse of healthcare data exchange. With an estimated 95% of U.S. healthcare organizations still relying on it, HL7v2 is the standard that keeps most legacy EHRs, lab systems, and billing platforms talking. It’s incredibly powerful, but its message-based structure can be rigid and a real headache to work with.
- DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine): As the name implies, DICOM is the global standard for everything related to medical imaging. It governs how MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays are formatted and exchanged, ensuring a radiologist in one hospital can actually view an image taken at another.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): FHIR is the modern, API-first standard that’s completely changing the game. It’s built on the same web technologies (like RESTful APIs) that power the apps on your phone. Instead of complex, monolithic messages, FHIR breaks data into logical "resources"—like a Patient, a Medication, or an Observation—making it far more flexible and developer-friendly.
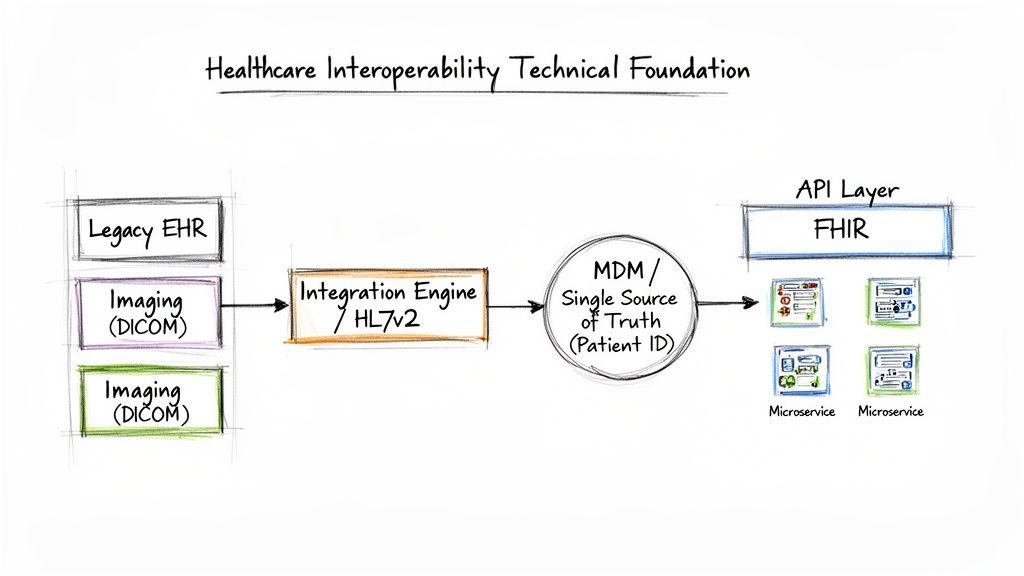
The real strategic goal isn't to pick one standard to rule them all. A truly robust architecture uses each for what it does best—HL7v2 for connecting legacy systems, DICOM for images, and FHIR as the flexible, forward-looking layer for modern applications and data sharing.
To help you decide where each standard fits into your strategy, here's a quick comparison of their strengths and primary roles.
Comparing Key Healthcare Data Standards
A practical comparison of common healthcare data standards, their primary uses, and key characteristics to guide your strategic decisions.
| Standard | Primary Use Case | Data Format | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| HL7v2 | Legacy system integration (EHR, LIS, billing) | Pipe-and-hat delimited text messages | Ubiquitous support across existing healthcare IT systems |
| DICOM | Medical imaging (MRI, CT, X-ray) storage and exchange | Binary format with metadata | The universal standard for all imaging modalities and equipment |
| FHIR | Modern application development, mobile apps, patient access | JSON, XML, RDF (RESTful APIs) | Highly flexible, web-friendly, and easy for modern developers to use |
Choosing the right standard for the right job is the first step. The next is building the architecture that puts them to work.
Designing Your Integration Architecture
With your standards selected, the next step is designing the "nervous system" that actually moves the data. There are really two primary architectural models to consider, each with its own set of trade-offs.
A centralized integration engine (often called an enterprise service bus or ESB) acts as a central hub. All data flows through it, where it can be transformed, routed, and monitored. This approach gives you strong control and visibility, but it can also become a bottleneck if it isn't managed carefully.
On the other hand, a decentralized, microservices architecture breaks down the exchange of data into smaller, independent services. For instance, one service might handle patient demographics, while another handles lab results. This model is incredibly scalable and resilient, but it demands more complex management and orchestration. As you evaluate the technologies for your solution, it's helpful to explore popular tech stack examples to see what modern patterns look like.
The Non-Negotiable Role of Master Data Management
Of all the technical components, Master Data Management (MDM)—specifically for patient identity—is arguably the most critical. In a disconnected system, a single patient often has multiple, slightly different records: Jane Smith at her PCP, J. Smith at the specialist, and Jane A. Smith at the hospital.
MDM solves this by creating a single source of truth. An MDM system uses sophisticated algorithms to find, link, and merge these duplicate records, creating a unique Master Patient Index (MPI). This isn't just a nice-to-have; it's non-negotiable.
Without a reliable MPI, all your interoperability efforts are built on a foundation of sand. You risk attaching a lab result to the wrong Jane Smith, creating serious patient safety risks and completely corrupting your analytics. A solid MDM and MPI strategy ensures data integrity from the ground up.
This trust in your data is also fundamental for deploying advanced AI tools for business that rely on clean, accurate information. You can learn more about how to unlock the value in your documents with our AI-Powered Data Extraction Engine.
Security and Governance: The Foundation of Trust
When you start connecting systems and sharing data, your security and governance have to be rock-solid. It's a simple equation: the more you open the door for data to flow, the stronger the locks need to be. This is about more than just dodging fines; it’s about earning the trust of patients and partners. Without that trust, your entire connected ecosystem is just a house of cards.
You’ve got to master the big regulations, of course—think HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe. But real security isn’t about checking boxes on a compliance form. It's about building a proactive, multi-layered defense that anticipates threats.
Going Beyond the Compliance Checklist
A modern security strategy for an interconnected health system can't be passive. You have to actively protect data everywhere it lives and everywhere it travels. That means putting specific, robust controls in place to ensure only the right people see the right information at the right time.
Here’s what that looks like on the ground:
- Tightly-Gated Access Controls: Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to enforce the principle of least privilege. A cardiologist doesn’t need to see a patient’s psychiatric notes, and a billing clerk certainly doesn't. Lock it down.
- End-to-End Encryption: This is non-negotiable. Whether data is sitting in a database or flying across the network through an API, it must be encrypted with strong, current protocols. No exceptions.
- Detailed Audit Trails: You need to be able to trace every touchpoint. Who accessed patient data? When? What did they view or change? This isn't just for breach investigations; it's about creating a culture of accountability.
Getting the details right on managing sensitive information is absolutely critical. For a deeper look into the specifics, a guide on HIPAA Compliant Document Management can offer some really practical guidance. These technical measures are the foundation of a system anyone can trust.
Why Strong Data Governance is Your Secret Weapon
If security is about keeping bad actors out, governance is about managing your data as a strategic asset from the inside. Think of it as the rulebook that allows everyone to share data confidently and efficiently. A good governance framework answers the tough questions before they turn into five-alarm fires.
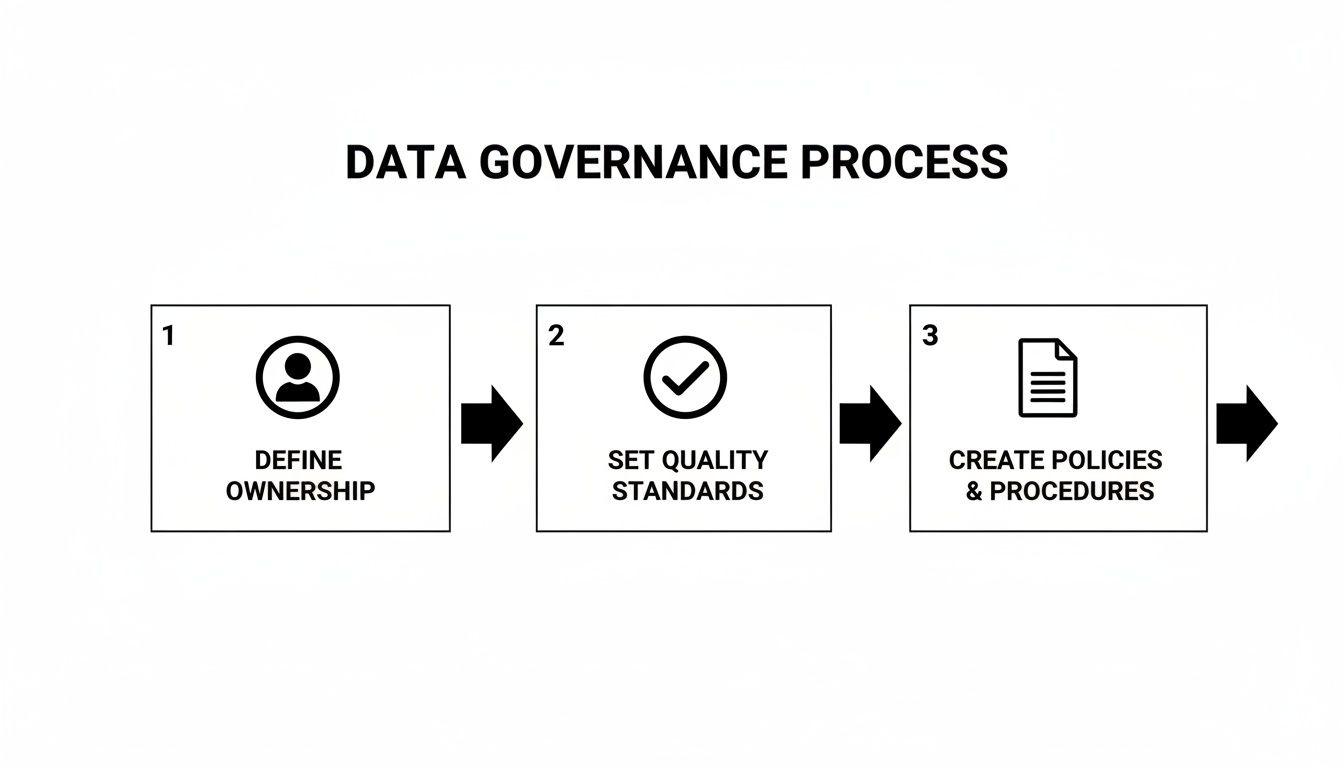
I've seen it work best when it's built on these three pillars:
- Define Clear Ownership: Every single data element—from a lab result to a billing code—needs a designated owner. This is the person or department on the hook for its accuracy, quality, and proper use.
- Set Data Quality Standards: You have to establish measurable rules for what "good" data looks like. Is it complete? Is it accurate? Is it timely? Bad data leads to bad clinical decisions and worthless analytics.
- Create Sharing Policies: Write down, in plain language, who can access what data, for what specific purpose, and under which conditions. No ambiguity.
A well-defined governance plan is the constitution for your healthcare data interoperability strategy. It provides the clarity and rules of engagement needed to scale your efforts without introducing chaos or risk.
Let's be honest: regulatory pressure is what’s really pushing this forward. In the U.S., the 21st Century Cures Act now dangles fines of up to $1 million per violation for information blocking, forcing providers to finally open up their data with standard FHIR endpoints. And when TEFCA (Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement) officially went live, it quickly onboarded over 625 hospitals, proving that a nationwide exchange isn't just a pipe dream anymore.
This isn’t just about compliance; it's about building a future-proof foundation. You can't get the benefits of advanced AI solutions or build sophisticated custom healthcare software development on a shaky base of poorly managed, insecure data. By getting security and governance right from the start, you’re not just meeting regulations—you’re building a resilient and trustworthy health ecosystem.
From Plan to Action: Rolling Out Your Strategy
Alright, you've done the hard work of building the strategy. Now comes the exciting part: making it real. A common mistake is trying to do everything at once. Big-bang rollouts in healthcare IT are incredibly risky and rarely go as planned. Instead, we're going to be smart about this. We’ll roll out the strategy in deliberate phases, which lets you learn as you go, show some early wins, and build momentum.
The best way to start is with a pilot project. Think of this as your proof of concept—your chance to show everyone that this isn't just theory and to earn some serious organizational trust.
Start with a High-Impact Pilot
The key here is to start small but aim for a big impact. Look for a narrow, well-defined problem that creates real, daily headaches for your clinicians or administrative staff. A classic example I've seen work wonders is automating the flow of lab results between a high-volume outpatient clinic and its main hospital. It’s a notorious bottleneck that grinds patient care to a halt and burns out staff.
To make sure your pilot knocks it out of the park, you need to be strategic.
- Find the Friction: Hunt for those workflows bogged down by manual data entry, endless phone tag, and fax machines. Fixing the referral process between primary care and specialists is another fantastic candidate.
- Keep it Focused: It's tempting to try and fix everything at once. Resist that urge. The goal is to prove one thing works perfectly before you even think about expanding.
- Find Your Champions: Work with clinical and administrative teams who are genuinely fired up about the project. You need partners who are not only excited but also willing to give you unfiltered, honest feedback.
With a solid use case in hand, it's time to define what success actually looks like. This goes beyond just technical milestones; we need to track the real-world impact your pilot is having. These metrics are what you'll use to build your business case for the next phase.
Define Your KPIs: What Gets Measured Gets Done
Success has to be tangible. Your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be directly tied to the problems you set out to solve. For that lab result pilot we talked about, your KPIs could be:
- Time to Access Patient Records: How long does it take a clinician to get a full patient history before and after your pilot? Taking that from 15 minutes down to 15 seconds is a story that tells itself.
- Fewer Duplicate Lab Orders: Track the drop in redundant tests ordered simply because the last results weren't available. This is a direct line to cost savings and better patient safety.
- Clinician Satisfaction: Survey your pilot group. Quantifying the improvement in their day-to-day workflow and job satisfaction is incredibly powerful.
These initial KPIs will set the stage for the broader metrics you'll use across the entire enterprise. It’s a cycle of continuous improvement—a core part of our AI Product Development Workflow—ensuring each phase is smarter than the last.
Dealing with Legacy Systems and Vendors
Let's be honest: one of the biggest headaches is getting shiny new tech to cooperate with your old, clunky systems. Your pilot will almost certainly have to plug into a legacy EHR or some other piece of existing infrastructure. This is where your vendor strategy becomes non-negotiable. When you're picking partners for the pilot, go with vendors who have a proven track record of integrating with a messy mix of systems, especially those offering flexible, API-first solutions.
The pilot is your controlled experiment for vendor relationships. It’s where you find out who your true partners are and who just creates more problems than they solve.
The push for interoperability is massive. The global market is expected to jump from USD 4.47 billion in 2025 to USD 11.69 billion by 2033. This isn't just tech for tech's sake; organizations are finally realizing that connectivity is a core business need. A huge driver of this is that 65% of hospitals in fast-moving markets are actively replacing or upgrading their EHRs, forcing vendors to get serious about modern, open standards. You can dig into the full report on this from Data Bridge Market Research.
Data governance is the backbone of this entire effort. Without it, even the best tech will fail.
This process ensures that as you connect more systems, you're not just creating more chaos. You're maintaining clear accountability and high-quality data across the board.
Your Playbook for Going Big
The insights you gain from your pilot—what worked, what broke, and which vendors were all-stars—are invaluable. You need to capture all of it. Consolidate this knowledge into a detailed implementation playbook.
This playbook becomes your roadmap for a repeatable, scalable, and predictable rollout across the entire organization. It should have everything from the nitty-gritty technical integration steps to communication plans and training guides.
By taking your strategy from paper to practice one phase at a time, you build a resilient, interconnected ecosystem for the future. This methodical approach, guided by real-world data and insights from our expert team, is how you achieve success that actually lasts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When you start digging into a healthcare data interoperability strategy, a lot of questions pop up. It’s a complex field, but getting clear answers is the first step toward making real progress. Here are some of the most common questions we hear from healthcare leaders.
What is the biggest challenge in healthcare interoperability?
Honestly, the biggest challenge is almost never the technology. It's the people and the politics. While wrestling with standards like FHIR is part of the job, the real fight is getting everyone on the same page. Different departments have their own priorities, legacy systems have been in place for decades, and change is just plain hard. Without strong, unwavering executive leadership driving a unified vision, the best technical plan in the world will stall out.
How is FHIR different from HL7v2?
Think of it this way: HL7v2 is like a fax machine, and FHIR is like a modern web API. Both get information from point A to point B, but one is far more flexible and easier for today's developers to use. HL7v2 is message-based and rigid, often requiring specialized, hard-to-find expertise. FHIR, on the other hand, is built on the same web standards that power the internet (like RESTful APIs). It breaks data down into logical chunks called "resources"—like a Patient, a Medication, or an Observation. This modern approach lets an application ask for only the specific piece of data it needs, which is a game-changer for building the next generation of Healthcare AI Services.
How do you measure the ROI of an interoperability project?
You can’t just hope for a good return on investment—you have to prove it. The key is tying your interoperability goals to tangible business and clinical outcomes right from the start. Track metrics across three core areas:
- Financial Wins: Reductions in duplicate lab tests, decreased average length of stay, and shorter billing cycles.
- Operational Gains: Time saved by clinical staff, improved patient throughput, and more efficient referral processing.
- Clinical & Safety Improvements: Reductions in medical errors, better adherence to treatment protocols, and improved patient outcomes. By setting a baseline for these KPIs before you start, you can build a powerful story showing the real-world value of connected data. You can see how these metrics come to life in these real-world use cases.
What is the first step in creating an interoperability strategy?
Before you write a single line of code or evaluate a single vendor, assemble a cross-functional team. This isn't just an IT project; it's a clinical and business transformation. You need clinicians, administrators, billing specialists, and IT experts all in the same room. Your first task is to map out your current reality by identifying the biggest data-related pain points. This discovery work gives you the evidence you need to pinpoint achievable goals and build a business case that leadership can't ignore, a process that mirrors the deep dive we do in an AI requirements analysis.
How does AI enhance healthcare interoperability?
AI acts as a powerful catalyst for interoperability. While standards like FHIR create the "pipes" for data to flow, AI provides the "brain" to understand and use that data. For example, Natural Language Processing (NLP) can extract structured information from unstructured clinical notes, and machine learning models can predict patient risks based on integrated data from multiple sources. As we explored in our AI adoption guide, AI turns connected data into actionable insights, driving better clinical decisions and operational efficiency.
Ready to turn your data from a liability into your greatest strategic asset? Ekipa AI provides expert AI strategy consulting to guide healthcare organizations in building and launching powerful interoperability roadmaps. Our approach is backed by deep industry knowledge and a proven track record, delivered by our expert team. Let's design a more connected future for your organization, together.