A Guide to Healthcare Data Lifecycle Management
Master healthcare data lifecycle management with our complete guide. Learn the key stages, security, compliance, and how AI is revolutionizing data strategy.
Healthcare Data Lifecycle Management (HDLM) isn't just an IT task; it’s the entire journey of patient data, from the moment it’s created to the day it’s securely erased. Think of it less like a file in a cabinet and more like a living, breathing record that needs careful attention at every single step.
This methodical approach is a core business strategy, essential for keeping patients safe, running an efficient organization, and staying on the right side of the law.
Understanding The Healthcare Data Lifecycle
At its heart, managing the healthcare data lifecycle is about treating information as one of your most valuable assets. Every bit of patient data—whether it's a doctor's note in an Electronic Health Record (EHR), a complex lab result, or a simple insurance claim—has a story. That story needs a good steward.
This journey must be managed with precision to protect patient privacy, maintain the integrity of the information, and satisfy strict regulations like HIPAA. A single misstep at any point in the lifecycle can lead to devastating consequences, from patient harm and steep legal penalties to a complete erosion of trust. It’s a shift from a reactive, "store it and forget it" mentality to a proactive, strategic one. It's about always knowing what data you have, where it lives, who's allowed to see it, and when it's time to say goodbye for good. For a wider view of these principles, the concepts behind Information Life Cycle Management are a great starting point.
To give you a quick snapshot, here's a look at the distinct phases that make up this critical process.
The 6 Core Stages of the Healthcare Data Lifecycle
This table provides a quick overview of the essential stages in managing healthcare data, summarizing the primary goal of each phase in a clinical context.
| Lifecycle Stage | Key Objective in Healthcare |
|---|---|
| Create/Capture | Accurately record patient information at the point of care. |
| Store | Securely maintain data in compliant and accessible systems. |
| Use | Apply data for clinical decisions, billing, and analytics. |
| Share | Exchange information securely with authorized providers & systems. |
| Archive | Move inactive data to long-term, cost-effective storage. |
| Dispose | Securely and permanently delete data that's no longer needed. |
Each of these stages comes with its own set of rules and risks, which is why a formal management plan is so crucial.
Why A Managed Lifecycle Is Non-Negotiable
A solid HDLM framework isn't a "nice-to-have." For any modern healthcare provider, it's a fundamental requirement. Without one, you're flying blind, risking data breaches, operational chaos, and the inability to turn your vast amounts of data into meaningful, life-saving insights.
The upsides are tangible and felt across the entire organization.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: A structured lifecycle is your roadmap for meeting legal standards like HIPAA and GDPR. It makes audits less painful and dramatically cuts the risk of fines.
- Improved Patient Safety: Good clinical decisions depend on good data. Proper data management ensures that doctors and nurses have accurate, complete, and readily available information when it matters most.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: By systematically clearing out redundant, obsolete, and trivial (ROT) data, you can slash storage costs and simplify workflows. Your staff can find what they need, when they need it.
- Strengthened Data Security: A well-managed lifecycle shrinks your organization's attack surface. It establishes clear rules for who can access, use, and destroy data, building a stronger defense against breaches.
Ultimately, a robust HDLM strategy is the bedrock for building more advanced capabilities. It ensures the data that powers powerful tools, like those found in our Healthcare AI Services, is clean, compliant, and ready to fuel real innovation.
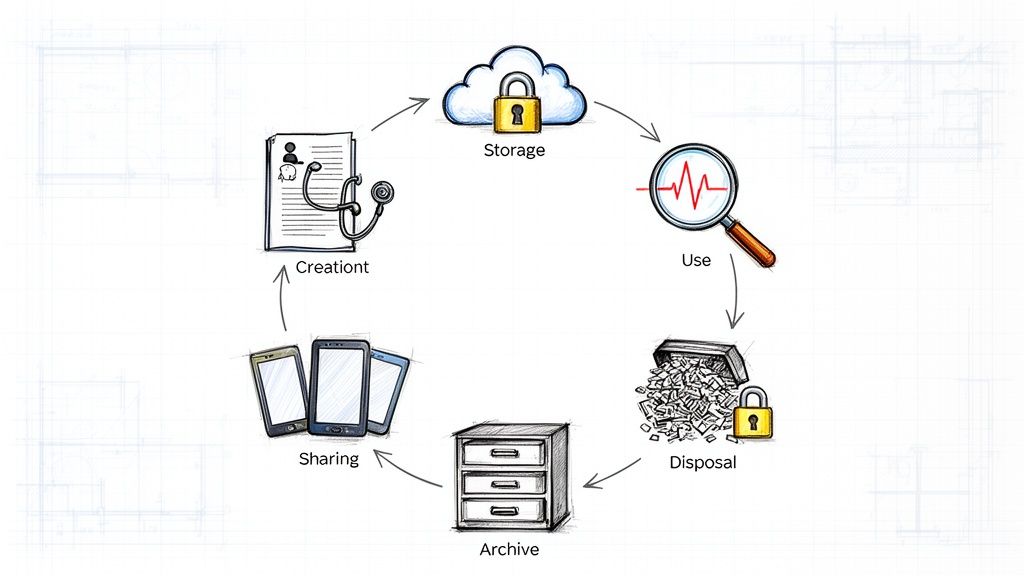
Navigating the Six Stages of the Data Lifecycle
Think of managing healthcare data like a patient's journey through a hospital. Data, just like a person, moves through distinct phases from the moment it’s "admitted" (created) to its final "discharge" (disposal). Each step comes with its own set of needs, risks, and rules. To protect the data's integrity and usefulness, every stage needs careful, deliberate management.
This structured process ensures that from the first entry to the final deletion, all healthcare information is handled securely, efficiently, and in full compliance.
The diagram above gives a high-level view of this journey: creating the record, managing its day-to-day life, and wrapping it in security. Now, let's dive into what each of the six stages really looks like on the ground.
Stage 1: Data Creation and Capture
This is the starting point, the birth of the data. It happens constantly and everywhere in a healthcare setting. A nurse records a patient's temperature. A surgeon types notes into an Electronic Health Record (EHR). A lab technician uploads blood test results. Data flows in from MRI machines, wearable fitness trackers, and even the billing department's administrative software.
The single biggest challenge here is data quality. One small error or omission at this initial stage can create a massive ripple effect down the line, leading to misdiagnoses, flawed research, and costly billing mistakes. Getting it right from the very beginning is absolutely critical.
Stage 2: Secure Storage
Once data exists, it needs a safe place to live. Healthcare organizations typically use a combination of their own on-premise servers and specialized, HIPAA-compliant cloud platforms. But it's not enough to just dump the data somewhere; it has to be actively protected with robust encryption, both when it's sitting "at rest" in a database and when it's "in transit" across a network.
Storing data isn't a passive activity. It requires active management to classify information based on sensitivity, implement access controls, and ensure that the storage environment meets stringent regulatory requirements.
With the volume of healthcare data projected to grow faster than in any other industry, having a modern, scalable storage solution is the foundation of any sound data strategy.
Stage 3: Active Use
This is where data gets to work and truly shows its value. It’s the most dynamic phase of its life. Physicians pull up EHRs to inform their diagnoses, billing staff use patient information to process claims, and researchers analyze anonymized datasets to spot public health trends.
The trick during this stage is to strike the right balance between easy access and tight security. The data has to be instantly available to authorized staff, but completely locked down for everyone else. This is usually handled with role-based access controls. For example, a surgeon can see clinical charts but not billing records (unless there's a specific need), and an administrator can see schedules but not sensitive patient notes. Fine-tuning this access is vital for patient care and smooth operations, a process that can be dramatically improved with the right internal tooling.
Stage 4: Controlled Sharing
Healthcare is a team sport. A family doctor needs to send a patient's file to a specialist. A hospital has to transmit data to a third-party lab. A clinic must report certain information to public health agencies. For patient care to be seamless, this sharing has to be both secure and efficient.
The greatest obstacle here is interoperability—or the lack of it. This is the ability for different IT systems and software to actually talk to each other and exchange data meaningfully. Without it, information gets stuck in digital silos, which can delay or even compromise patient care. Standardized formats like HL7 and FHIR, along with secure sharing protocols, are the keys to breaking down these barriers.
Stage 5: Strategic Archiving
Not all data needs to be at your fingertips forever. After a patient's case is closed or they haven't been seen in years, their records become inactive. Instead of letting this old data clog up expensive, high-performance systems, it gets moved to a secure, long-term archive. This cuts down on storage costs and helps active systems run faster.
But "out of sight" can't mean "out of mind." Archived data is still protected health information and remains subject to strict regulatory retention periods that can last for years, sometimes even decades. Your archiving strategy must guarantee that this data stays secure, uncorrupted, and retrievable in case of an audit, legal request, or the patient's return.
Stage 6: Defensible Disposal
The final stop. This is the permanent, secure destruction of data, and it can only happen after the legally required retention period is over. Just hitting "delete" on a file isn't nearly enough, as it often leaves behind recoverable fragments on a hard drive.
Proper disposal involves methods that make the data completely unrecoverable, such as physically shredding the drives or using cryptographic erasure techniques. A "defensible" process is one that leaves a clear audit trail, proving that the data was destroyed in a compliant and documented manner. This last step is just as crucial as the first, closing the loop on a responsible and secure healthcare data lifecycle management strategy.
Building Your Governance, Security, and Compliance Framework
A well-defined data lifecycle is a great start, but it can't operate in a vacuum. It needs a solid framework of governance, security, and compliance holding it up. These three pillars work in concert, turning the theory of healthcare data lifecycle management into a practical, defensible reality that protects both patients and your organization.
Let's think of it like building a house. Governance is the architect's blueprint, dictating the structure and purpose of every room. Security is the locks on the doors, the alarm system, and the reinforced walls. Compliance is the final inspection that proves the house is built to code and safe for people to live in. You simply can't have one without the others.
Governance: The Strategic Blueprint
Data governance is essentially the strategic rulebook for all your data. It’s about establishing crystal-clear ownership and accountability—defining who can access, create, change, or delete data, and under what specific circumstances. This isn't about locking information down; it's about making sure it's managed responsibly and consistently throughout its entire journey.
A strong governance program answers the tough questions up front:
- Who owns this data? The cardiology department might "own" its patient records, while the finance department owns billing data.
- What does "good" data look like? Governance sets the standards for accuracy, completeness, and timeliness.
- How can this data be used? It lays out the approved uses for different datasets, from direct clinical care to anonymized research.
This kind of strategic oversight is the bedrock. It ensures every stage of the data lifecycle follows a unified set of principles, which helps tear down data silos and build a culture of data responsibility. Our work in AI strategy consulting shows time and again that solid governance is the first, non-negotiable step to unlocking the real value of your data.
Security: The Protective Shield
If governance sets the rules, security is what enforces them with technical and physical safeguards. In healthcare, the mission is clear: protect Protected Health Information (PHI) from any unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This isn't just a best practice; it's the fundamental requirement for earning and keeping patient trust.
Key security measures have to be woven into every single stage of the lifecycle:
- Encryption: Data must be unreadable to unauthorized parties, both "at rest" (sitting in a database) and "in transit" (being sent across a network).
- Access Controls: Role-based access control (RBAC) is crucial. It ensures that clinicians, administrators, and billing specialists can only see the specific data they absolutely need to do their jobs—and nothing more.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Your systems need to keep a constant, detailed log of who accesses data, when they do it, and what they do with it. This creates an audit trail that is essential for spotting suspicious activity.
Together, these controls create a multi-layered defense that makes it incredibly difficult for threats—whether from outside or inside—to compromise sensitive patient information. For any organization undertaking custom healthcare software development, these security principles have to be baked in from the very first line of code.
Compliance: The Mandate for Trust
Compliance is the measurable proof that your governance and security practices are working. It's how you demonstrate that your organization adheres to the letter and spirit of regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It’s best to think of compliance not as a separate checklist, but as the natural result of doing everything else the right way.
HIPAA isn't just a set of rules to avoid fines; it’s a framework for building patient trust. When patients feel confident their most sensitive information is protected, they are more likely to engage openly with their care providers, leading to better health outcomes.
The business case for this level of discipline is no longer up for debate. Data quality has become a board-level strategic priority across U.S. healthcare. By 2026, top health systems will formally integrate their data quality strategy into enterprise risk management, because they recognize that bad data undermines both financial stability and clinical outcomes. This shift means treating data as a core strategic asset, not just an IT problem. You can explore more predictions on how the Intelligent Healthcare Ecosystem is evolving by reading the full analysis here.
Ultimately, this three-pillar framework turns data management from a simple cost center into a strategic advantage, fostering trust and preparing your organization for advanced analytics and AI. To see how these principles align with a structured implementation plan, connect with our expert team.
How AI and Automation Are Changing the Game
For years, healthcare data lifecycle management has been a manual, often clunky process. It’s slow, expensive, and frankly, full of opportunities for human error. But that's starting to change. The introduction of artificial intelligence and automation is turning these rigid, static workflows into something much more dynamic—an intelligent system that practically manages itself.
This isn't some far-off future concept; it's happening right now. By handing off the repetitive, routine tasks to machines, AI solutions let skilled professionals focus on what really matters. Instead of a data analyst spending half their day manually sorting and tagging new records, smart algorithms can do it instantly with a far higher degree of accuracy. It's a critical shift, especially with the sheer volume of health data being generated every single day.
AI is weaving its way into every single stage of the data lifecycle, bringing major upgrades in speed, security, and the quality of insights we can pull from the data.
Smarter Data Creation and Classification from Day One
AI starts adding value the second a piece of data is created. Think about a clinician typing notes into an Electronic Health Record (EHR).
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is where AI truly shines. It can read through unstructured text—like a doctor's free-form notes—and automatically identify and tag crucial information. It pulls out diagnoses, medications, and symptoms, turning a block of text into structured, usable data.
- Automated Data Validation: As data is being entered, AI can act as an instant quality check. It can flag potential mistakes or inconsistencies in real time. For instance, an algorithm could alert a nurse if a blood pressure reading seems physiologically impossible for a patient, preventing a critical error before it ever gets saved.
Getting this right at the source means less time spent later on cleaning up messy data, which makes it ready for analysis almost immediately.
From Static Storage to Predictive Power
In the "Use" and "Archive" stages, AI’s role shifts from simple organization to genuine prediction. Instead of just sitting in a digital warehouse, old data becomes a powerful tool for forecasting what might happen next. One of the most impactful real-world use cases for this is in predictive health analytics.
AI models can comb through years of archived patient data to spot patterns that identify individuals at high risk for conditions like sepsis or heart failure. This allows clinical teams to step in before a crisis happens. Suddenly, archived data isn't just a compliance headache; it's a dynamic asset for improving patient care. This is a core function of effective Healthcare AI Services.
Automating Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are probably where automation delivers its most immediate and obvious return on investment. With AI Automation as a Service, you get a level of round-the-clock vigilance that’s simply impossible to achieve with a human team alone.
An AI-powered security system can spot unusual activity that might signal a data breach—like an employee suddenly accessing hundreds of patient records they don't normally handle. This shrinks the response time from days or weeks down to minutes.
AI can also automate the entire data retention process. It knows when data has met its legal retention period and can automatically flag it for secure, defensible disposal. This not only tightens up security and minimizes risk but also helps control ever-growing storage costs. You can dive deeper into this by checking out our guide on AI automation.
The market is clearly taking notice. Projections show the clinical data management market is set to grow from USD 3.62 billion in 2025 to USD 10.89 billion by 2035, with AI-driven analytics being a primary driver. This explosive growth sends a clear signal: healthcare leaders who aren't building a scalable data infrastructure now risk being left behind. You can explore more about these market projections on Precedence Research.
Your HDLM Implementation Roadmap
Putting a real healthcare data lifecycle management program in place doesn't happen overnight. It’s a deliberate journey, not a sprint. If you rush it or roll out a half-baked plan, you risk disrupting clinical workflows and burning through your budget with little to show for it. A phased approach is the only way to ensure a smooth transition, keep risks in check, and build momentum that lasts.
Think of this roadmap as a practical blueprint for getting from A to B. It breaks the process down into four manageable phases, moving from initial discovery to full-scale rollout and ongoing improvement. It's a disciplined process, much like you'd find in a well-run AI Product Development Workflow.
Phase 1 The Assessment
Before you can build anything new, you have to know exactly what you're working with. This first phase is pure discovery. Your goal is to map out your entire data landscape—where information lives, how it moves through your systems, and where your biggest vulnerabilities and opportunities are hiding. Without this baseline, you're just guessing.
Here’s what you’ll be doing:
- Data Auditing: Get your arms around every data asset you have. This means cataloging everything from your Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and PACS imaging systems to billing platforms and third-party data feeds.
- Process Mapping: Go talk to people. Sit down with department heads and frontline staff to understand how data is actually created, used, and shared in their day-to-day work, not just how the manual says it should be.
- Risk Identification: Start looking for the red flags. Pinpoint compliance gaps, security weak spots like unencrypted data stores, and the operational headaches caused by bad data.
Phase 2 The Strategy
Once you have a clear picture of your current state, it’s time to design the future. This is where you turn your findings from the assessment into a formal HDLM strategy. You’ll be setting clear goals, defining the rules of the road with governance policies, and getting key stakeholders on board. Remember, this isn't just an IT project; it's a core business strategy.
A strong HDLM strategy isn't built in a vacuum. It has to connect directly to what your organization is trying to achieve. Whether your top priority is improving patient outcomes, cutting operational costs, or powering new research, your data strategy must serve that mission.
What this phase looks like in practice:
- Defining Objectives: Set specific, measurable goals. Think things like, "We will reduce data storage costs by 15% within 18 months," or "We will achieve a 99% data accuracy rate for all new patient records."
- Establishing Governance: Formalize how data will be managed. This means creating a data governance committee and drafting clear policies that define data ownership, set quality standards, and spell out access rules.
- Building the Business Case: Show leadership the money. Articulate the clear return on investment, connecting the dots between better data management and better business outcomes.
The financial justification is often more powerful than you'd think. Consider that programs aimed at reducing hospital-acquired conditions—which lean heavily on high-quality clinical data—saved the U.S. healthcare system an estimated USD 19.9 billion between 2010 and 2014. These numbers prove that investing in data infrastructure isn't just a cost; it delivers real financial and clinical value. To see how these trends will influence future plans, you can explore the full registry data analysis.
Phase 3 Technology and Tool Selection
You’ve defined the "why" with your strategy and the "what" with your governance policies. Now it's time to figure out the "how." This phase is all about choosing the right infrastructure and tools to make your HDLM plan a reality. You'll evaluate your existing technology stack, identify the gaps, and decide whether to upgrade current systems or bring in new solutions.
The right AI tools for business can be a game-changer here, automating tedious tasks from data classification to security monitoring. When you're evaluating vendors, focus on scalability, how well a new tool will play with your existing systems (especially your EHR), and, above all, the vendor's unwavering commitment to HIPAA compliance.
Phase 4 Implementation and Monitoring
With the planning done, it’s time to execute. This final phase is about rolling out your new policies, processes, and technologies in a controlled, manageable way. A "big bang" launch is usually a recipe for disaster. Instead, start with a pilot program in a single department to work out the kinks before going live across the entire organization.
As you roll out the program, you have to keep score. Continuous monitoring is essential. Track the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) you defined back in the strategy phase to measure your progress. Metrics like data quality scores, compliance audit pass rates, and storage cost reductions will give you the feedback you need to tweak your approach and prove the program's value to the rest of the organization. This cycle of implementing, measuring, and refining is what separates a short-term project from a long-term success.
Your Executive Checklist: Charting the Path Forward
Knowing about healthcare data lifecycle management is one thing; putting it into practice is another entirely. This checklist is built for leaders who need to cut through the noise and figure out where to start.
Think of these questions as conversation starters for your next leadership meeting. Use them to get an honest read on where you stand and what your immediate priorities should be. The goal is to find the gaps between where you are today and where you need to be to run a secure, efficient, and compliant operation.
Governance and Strategy
This is your foundation. Without a clear game plan and someone in charge, even the best technology will fall short.
- Is there a formal policy? Do we have a documented, board-approved data governance policy that specifically addresses healthcare data?
- Who owns the data? Has a specific person or team been assigned ownership for each key data area, like clinical, financial, and operational data?
- Does it align with business goals? Can we clearly connect our data management strategy to top-level objectives, like improving patient care or cutting operational waste?
Security and Compliance
These are the table stakes. Getting this wrong puts both your patients and the organization at serious risk.
- How strong is our end-to-end security? Are we auditing security controls at every single stage of the data lifecycle, from the moment data is created to when it’s destroyed?
- Who can access what? Are our role-based access controls actually working? We need to review them constantly to ensure people only see the minimum data they need to do their jobs.
- How do we handle data disposal? Is our process for destroying PHI documented, defensible, and fully compliant with HIPAA’s strict requirements?
Technology and Automation
This is where you make your processes smarter and more efficient. It’s about replacing manual effort with intelligent systems.
- Are we automating the right things? Are we still relying on people to classify data, enforce retention rules, and spot security threats? This is where mistakes happen. A smart AI Automation as a Service partner can significantly cut down on human error.
- Are our systems talking to each other? Do our core platforms—EHR, PACS, billing systems—work together smoothly, or is our most valuable data stuck in isolated silos?
- Is our tech ready for the future? Can our current data infrastructure handle what’s next, like predictive analytics and more advanced AI solutions? An AI requirements analysis is the best way to find out for sure.
Moving from discussion to action is what matters most. To build an organization that truly runs on data, you need a clear plan. A Custom AI Strategy report can provide that roadmap, or you can talk directly with our expert team to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're knee-deep in managing healthcare data, a lot of questions come up. It's a complex world, so let's tackle some of the most common ones that leaders ask when they're building out their data strategy.
What Is the Most Challenging Stage of the Healthcare Data Lifecycle?
If you ask ten healthcare IT leaders, nine will likely point to the "Share" and "Use" stages. Every other stage has its challenges, of course, but this is where the rubber really meets the road.
The central tension is trying to make data instantly available for a doctor who needs it right now while also keeping that same data locked down to meet strict HIPAA rules. Think about it: getting a hospital's EHR system to talk seamlessly with a specialist's office software is already a massive technical hurdle. Doing it without compromising data integrity or security? That’s the persistent headache for nearly everyone in the field.
How Does HIPAA Affect Healthcare Data Disposal?
HIPAA is crystal clear and unforgiving when it comes to getting rid of old data. The rule is simple: any Protected Health Information (PHI) must be destroyed so thoroughly that it's impossible to read, piece back together, or figure out in any way.
This isn't like dragging a file to the recycling bin on your desktop. That's a huge compliance risk. We're talking about methods that are permanent and defensible, like physically shredding hard drives into tiny pieces or using cryptographic software to overwrite the data until it's gone for good.
If you need a deeper dive, this guide on IT equipment disposal HIPAA requirements is a great resource.
Can We Use a Public Cloud for Storing Patient Data?
Absolutely, but you have to do it the right way. Storing patient data on a public cloud like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure is common practice, but only if two conditions are met. First, the cloud provider must offer a HIPAA-compliant service tier. Second, and this is non-negotiable, they must sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with you.
The BAA is a critical legal document. It essentially makes the cloud provider just as responsible for protecting your patient data as you are. Without it, you’re out of compliance. An AI strategy consulting tool can be incredibly helpful for figuring out which provider and service configuration makes the most sense for your specific needs.
What Is the First Step to Creating an HDLM Strategy?
Before you write a single policy, you need to start with a comprehensive data audit. You simply can't manage what you don't know you have. This isn't a quick task; it's a deep-dive investigation.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Identify every single type of data you handle—from patient charts and lab results to billing information and imaging files.
- Map out exactly where all this data lives. Is it on-prem servers? In the cloud? On specific workstations?
- Document the complete journey of the data. Follow it from creation to disposal, noting who touches it and when.
This foundational audit gives you the clear map you need to spot security gaps, design smart governance rules, and build a healthcare data lifecycle management framework that actually works.
At Ekipa AI, we help turn these kinds of complex data problems into real strategic assets. Our platform is designed to help you build and roll out an AI strategy that boosts efficiency, keeps you compliant, and finds new value hidden in your data. See how our AI solutions can create the data-driven foundation your organization needs to thrive. The success of these solutions is driven by the expertise and dedication of our expert team, who bring deep industry knowledge to every project.